GOTHROUGH ABOUT INCOME TAX RETURNS (ITR)
WHAT IS ITR ?
- Income Tax Return (ITR) is a form in which the taxpayers file information about his income earned and tax applicable to the income tax department.
- The department has notified 7 various forms, i.e. ITR 1, ITR 2, ITR 3, ITR 4, ITR 5, ITR 6 & ITR 7 till date.
- Every taxpayer should file his ITR on or before the specified due date.
- The applicability of ITR forms varies depending on the sources of income of the taxpayer, the amount of the income earned and the category the taxpayer belongs to like individuals, HUF, company, etc.
ITR-1
- This Return Form is for a resident individual whose total income for the assessment year 2021-22 includes:
- Income from Salary/ Pension; or
- Income from One House Property (excluding cases where loss is brought forward from previous years); or
- Income from Other Sources (excluding Winning from Lottery and Income from Race Horses)
- Agricultural income up to Rs.5000.
v Who cannot use ITR 1 Form?
- Total income exceeding Rs 50 lakh
- Agricultural income exceeding Rs 5000
- If you have taxable capital gains
- If you have income from business or profession
- Having income from more than one house property
- If you are a Director in a company
- If you have had investments in unlisted equity shares at any time during the financial year
- Owning assets (including financial interest in any entity) outside India, if you are a resident, including signing authority in any account located outside India
- If you are a resident not ordinarily resident (RNOR) and non-resident
- Having foreign assets or foreign income
- If you are assessable in respect of income of another person in respect of which tax is deducted in the hands of the other person.
ITR-2
v ITR 2 is for the use of an individual or a Hindu Undivided Family (HUF) whose total income for the AY 2021-22 includes:
- Income from Salary/Pension; or
- Income from House Property; or
- Income from Other Sources (including Winnings from Lottery and Income from Race Horses).
- Total income from the above should be more than Rs 50 Lakhs
- If you are an Individual Director in a company
- If you have had investments in unlisted equity shares at any time during the financial year
- Being a resident not ordinarily resident (RNOR) and non-resident
- Income from Capital Gains; or
- Foreign Assets/Foreign income
- Agricultural income more than Rs 5,000
- Further, in a case where the income of another person like one’s spouse, child etc. is to be clubbed with the income of the assesses, this Return Form can be used where such income falls in any of the above categories.
Ø Who cannot use this Return Form
- This Return Form should not be used by an individual whose total income for the AY 2021-22 includes Income from Business or Profession. For declaring these types of incomes, you may have to use ITR-3 or ITR-4 .
ITR-3
- The Current ITR3 Form is to be used by an individual or a Hindu Undivided Family who have income from proprietary business or are carrying on profession. The persons having income from following sources are eligible to file ITR-3 :-
- Carrying on a business or profession
- If you are an Individual Director in a company
- If you have had investments in unlisted equity shares at any time during the financial year
- Return may include income from House property, Salary/Pension and Income from other sources
- Income of a person as a partner in a firm
ITR-4
- The current ITR 4 is applicable to individuals and HUFs, Partnership firms (other than LLPs) which are residents having income from a business or profession.
- It also includes those who have opted for the presumptive income scheme as per Section 44AD, Section 44ADA and Section 44AE of the Income Tax Act.
- However, if the turnover of the business exceeds Rs 2 crore, the taxpayer will have to file ITR-3.
Ø Who cannot use ITR 4 Form?
- If your total income exceeds Rs 50 lakh
- Having income from more than one house property
- If you have any brought forward loss or loss to be carried forward under any head of income
- Owning any foreign asset
- If you have signing authority in any account located outside India
- Having income from any source outside India
- If you are a Director in a company
- If you have had investments in unlisted equity shares at any time during the financial year
- Being a resident not ordinarily resident (RNOR) and non-resident
- Having foreign assets or foreign income
- If you are assessable in respect of income of another person in respect of which tax is deducted in the hands of the other person.
ITR-5
- ITR 5 is for firms, LLPs (Limited Liability Partnership), AOPs (Association of Persons), BOIs (Body of Individuals), Artificial Juridical Person (AJP), Estate of deceased, Estate of insolvent, Business trust and investment fund.
ITR-6
- For Companies other than companies claiming exemption under section 11 (Income from property held for charitable or religious purposes), this return has to be filed electronically only.
ITR-7
- For persons including companies required to furnish return under section 139(4A) or section 139(4B) or section 139(4C) or section 139(4D) or section 139(4E) or section 139(4F).
- Return under section 139(4A) is required to be filed by every person in receipt of income derived from property held under trust or other legal obligation wholly for charitable or religious purposes or in part only for such purposes.
- Return under section 139(4B) is required to be filed by a political party if the total income without giving effect to the provisions of section 139A exceeds the maximum amount, not chargeable to income-tax.
- Return under section 139(4C) is required to be filed by every –
- Scientific research association;
- News agency ;
- Association or institution referred to in section 10(23A);
- Institution referred to in section 10(23B);
- Fund or institution or university or other educational institution or any hospital or other medical institution.
- Return under section 139(4D) is required to be filed by every university, college or other institution, which is not required to furnish return of income or loss under any other provision of this section.
- Return under section 139(4E) must be filed by every business trust which is not required to furnish return of income or loss under any other provisions of this section.
- Return under section 139(4F) must be filed by any investment fund referred to in section 115UB. It is not required to furnish return of income or loss under any other provisions of this section.
|
TYPES OF ITR FORM IN SUMMARISED MANNER
|
||||||||||
|
ITR Form |
Applicable to |
Salary |
House Property |
Business Income |
Capital Gains |
Other Sources |
Exempt Income |
Lottery Income |
Foreign Assets/Foreign Income |
Carry Forward Loss |
|
ITR 1 |
Individual, HUF (Residents) |
Yes |
Yes(One House Property) |
No |
No |
Yes |
Yes (Agricultural Income less than Rs 5,000) |
No |
No |
No |
|
ITR 2 |
Individual, HUF |
Yes |
Yes |
No |
Yes |
Yes |
Yes |
Yes |
Yes |
Yes |
|
ITR 3 |
Individual or HUF, partner in a Firm |
Yes |
Yes |
Yes |
Yes |
Yes |
Yes |
Yes |
Yes |
Yes |
|
ITR 4 |
Individual, HUF, Firm |
Yes |
Yes(One House Property) |
Presumptive Business Income |
No |
Yes |
Yes (Agricultural Income less than Rs 5,000) |
No |
No |
No |
|
ITR 5 |
Partnership Firm/ LLP |
No |
Yes |
Yes |
Yes |
Yes |
Yes |
Yes |
Yes |
Yes |
|
ITR 6 |
Company |
No |
Yes |
Yes |
Yes |
Yes |
Yes |
Yes |
Yes |
Yes |
|
ITR 7 |
Trust |
No |
Yes |
Yes |
Yes |
Yes |
Yes |
Yes |
Yes |
Yes |
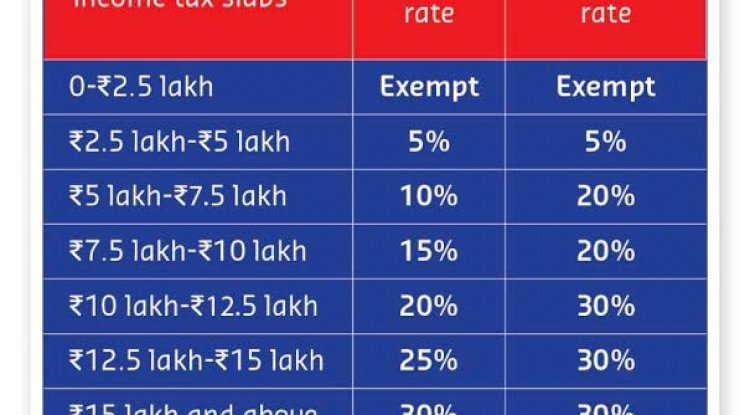
SLAB RATES NOW & BEFORE
Deductions
Section 80C Deductions to be deducted while computing total income for Financial Year (F.Y 2020-21)/ Assessment Year 2021-22 (A.Y 2021-22)
The aggregate amount of deductions allowed under section 80C (along with 80CCC & 80CCD) is INR 1,50,000. The deductions under section 80C are allowed only to the following assessees:-
- Individual
- Hindu Undivided Family
Following are the Savings/ Investments covered under section 80C where we can invest which are allowed to be deducted from the total income:- (Maximum deduction which can be claimed under this section is INR 1,50,000)
(i). LIFE INSURANCE POLICY:-
Investment in a Life insurance policy to keep in force an insurance on the life of:-
- Individual Himself
- His/Her Spouse
- Child of such Individual*
* Child may be married/unmarried, dependent or not on the Individual.
For HUF – A deduction would be allowed on the premium paid by HUF for any of its members of the family.
However, there are certain limits on the amount of premium eligible for deduction with respect to the premium paid on an insurance policy which is as follows:-
(a)
*Capital Sum Assured refers to the value of insurance cover provided at the time of buying the insurance policy. In case of any eventuality, like death, the sum assured is the amount that is paid to the beneficiary.
(b). There is a minimum holding period of 2 years that needs to be fulfilled in order to claim a deduction for life insurance premium paid under section 80C. Where the Life Insurance Policy is terminated or sold etc before the minimum holding period of 2 years then the deduction allowed in earlier years would be deemed as income of the previous year in which such policy is terminated or sold etc.
(ii) Any payment made by the individual only to effect or keep in force a contract of non-commutable deferred annuity* for any of the following person:-
– Individual Himself
– His/Her Spouse
– Child of such individual
Provided that such contract does not contain a provision for the exercise by the insured of an option to receive a cash payment in lieu of payment of the annuity.
* Non-Commutable Deferred Annuity:- It is a non-transferable contract with an insurance company that promises to pay the owner a regular income, or a lump-sum amount at some future date.
(iii). Sum deducted by or on behalf of the government:- Any sum deducted by or on behalf of the government –
(a). From salary payable of such individual
(b). For purpose of securing to him a deferred annuity or
(c). Making provision for his spouse or children.
(d). However, the sum deducted from salary payable shall not exceed 1/5th of Salary.
(iv). Statutory Provident Fund or Recognized Provident Fund:-
Statutory Provident Fund– This fund is maintained by a Government and Semi-Government organization.
– Govt. employee contributes a certain amount from their salary to this fund.
– Accumulation to this fund is paid to the govt. employee at the time of retirement or superannuation.
– This fund is also termed as GPF (i.e Government Provident Fund) therefore only govt. employees can contribute in this fund and not private sector employees.
Recognized Provident Fund– This fund is recognized by commissioner of income tax as per the rules and provisions contained in income tax act.
– Here it covers EPF (i.e employee provident fund)
– Employer deduct some portion from the salary of it’s employee and deposit it in EPF account along with it’s own contribution in the name of employee which the employee will get at the time of retirement.
(v). PUBLIC PROVIDENT FUND:-
Any contribution made by an individual (whether salaried or self employed) or HUF in PPF would be allowed as deduction from total income. Investment of Individual can be in the name of :-
– Individual himself
– His/Her Spouse
– Any Child of such individual (Dependent /not or Married/not)
Investment of H.U.F can be in the name of :-
– Any member of the Family.
(vi). Approved Superannuation Fund:-
Any contribution made by an employee in an approved superannuation fund would be allowed as deduction from total income.
*Approved superannuation fund:- It is a fund that is approved by the commissioner of income tax if certain conditions are fulfilled. You can even confirm from your employer whether your superannuation fund is approved or not.
(vii). Investment in schemes notified by Central Government:-
Any contribution made by an individual towards following schemes:-
(a). National Saving Scheme,1992
(b). Sukanya Samriddhi Account – Any sum deposited in the name of girl child under this scheme would be eligible for 80C deduction.
* Girl child may be individual’s daughter or for whom such individual is legal guardian.
(viii). National Savings Certificate:- (VIII OR IX ISSUE).:-
Any subscription made by an individual or HUF to National Saving Certificates would be eligible for deduction under section 80C. Where the interest accrued on such certificates is reinvested or deemed to be reinvested than such reinvested amount would also be eligible for deduction under this section.
(ix). Unit Linked Insurance Plan of Unit Trust of India:-
Any contribution made by individual or HUF in Unit Linked Insurance Plan of Unit Trust of India would be eligible for deduction.
In case of Individual, contribution made by individual for :-
- Individual himself
- His/Her Spouse
- Any child of such individual (Married/Unmarried, Dependent/Independent)
In case of HUF:- Any member of the HUF.
Unit Linked Insurance Plan of LIC Mutual Fund section 10(23D):-Any contribution made by individual or HUF in Unit Linked Insurance Plan of LIC mutual fund would be eligible for deduction.
In case of Individual, contribution made by individual for :-
- Individual himself
- His/Her Spouse
- Any child of such individual (Married/Unmarried, Dependent/Independent)
In case of HUF:- Any member of the HUF.
(x). Subscription to Notified Annuity Plan:-
Any subscription/contribution by individual or HUF to notified annuity plans of LIC or any other insurer would be eligible for deduction. Following are the Annuity plans which have been notified where we can invest and save our tax.:-
- New Jeevan Dhara
- New Jeevan Dhara-I
- New Jeevan Akshay
- New Jeevan Akshay-I
- New Jeevan Akshay-II
(xi). Equity Linked Saving Scheme,2005:-
Equity linked saving scheme is a category of mutual fund which provides dual benefits i.e Tax Savings and Capital Appreciation. ELSS comes under the category of Equity and therefore more than 65% of your amount would be invested in equity.
*It is having Minimum Lock-in Period of 3 Years which is less as compared to lock-in period of PPF, NPS which are having lock-in period of 5 years or more.
(xii). Notified Pension Fund:-
Any contribution made by an individual to a Notified Pension Fund would be eligible for deduction. One such notified pension fund is (RETIREMENT BENEFIT PENSION FUND)
(xiii). National Housing Bank:-
Any contribution made by an individual to any deposit scheme or contribution to any pension fund setup by national housing bank would be eligible for deduction. One such notified deposit scheme of the National Housing Bank is Home Loan Account Scheme.
(xiv). Tuition Fees of Children (Any 2 children):-
Where you have school going children, you can include in deduction their tuition fees which you have paid for the year to any university , college, school or other educational institution situated in India. The tuition Fees paid would be eligible for deduction only when it is paid for full-time education and not for open learning.
(xv). Home Loan (Deduction on Principal Repayment):-
Where an individual has taken home loan for purchase or construction of residential house property, then the principal portion of the EMI (Easy Monthly Installment made for repayment of such loan) paid for the year would be eligible for deduction under section 80C subject to certain conditions :-
- Such property shall not be sold for 5 years from the date of possession.
- Where the individual sold such house property before the period of 5 years than all the deductions which he had claimed in earlier years with respect to principal amount would be added back to his income in the year of sale.
* Also Payment made for Stamp Duty and Registration Fees can also be claimed as deduction along with principal amount (Subject to ceiling limit of INR 1,50,000) in the year in which it is paid.
(xvi). Investment in Equity Shares or Debentures:-
Where any individual or HUF subscribe to equity shares or debentures of any eligible issue of capital* of :-
- Public Company or
- Public Financial Institution
where proceeds from such issue of shares or debentures are utilized for infrastructure company.
* Eligible issue of Capital:- Means an issue of shares or debentures made by public company or public financial institution and the entire proceeds from such issue are utilized wholly & exclusively for purpose of infrastructure business referred to in section 80IA(4).
(xvii). Term Deposit:-
Any sum deposited by an individual or huf in a term deposit for a fixed period of not less than 5 years in any scheduled bank or any other bank constituted under banking companies act.
(xviii). NABARD Bonds:-
Deduction would be eligible for NABARD bonds purchased by an individual or huf .
*NABARD – National Bank for Agriculture and Rural Development.
(xix). Senior Citizen Saving Scheme:-
Any sum deposited by an individual or huf in a senior citizen saving scheme rules, 2004.
(xx). Time Deposit:-
Any sum deposited by individual or huf in a 5 years time deposit account under Post Office Time Deposit Rules, 1981.
(xxi). Pension Scheme under Section 80CCD:-
Only Central Government employees are eligible for this deduction and contribution shall have lock-in period of 3 years.
** All the above mentioned deductions would be eligible only on payment basis and not on due basis i.e it would be allowed as deduction only when it is actually paid during the previous year.
What's Your Reaction?























