STUDY OF INCOME TAX
What is Income Tax?
Income tax is a direct tax which is imposed by government as a legal charge on income of individuals or firms. It is defined under direct tax as it cannot be shifted from one person to another person and is paid only by person on whom it is actually levied, whether he is an individual, company or any other organization.
Defining the ‘Previous year’
Previous year or the financial year or your tax year is the 12 month period that begins on 1st April and ends on the 31st March of the next year.No Matter when you start business and job ,your tax year end 31st March and a new tax year starts on 1st April. So, it is important to plan your taxes for each financial year.
Assessment Year
It is a term you’ll often hear in relation to tax filing. It is the financial year after the previous year in which you will ‘assess’ and file your return for the previous year. So, assessment year is 2021-22 for the previous year 2020-21. Assessment year is the year in which you will file your return for the previous year. For instance, if you start your job on 1 January 2021, your tax year closes on 31 March 2021. 2020-21 is your previous year and your AY is 2021-22. The last day to file your return is 31 August 2021.
Understanding your Salary
When you start your job – reach out to your payroll or HR department and get your Salary details/ Pay Slip / Tax Statement. Here, you will get an idea of the major components of your salary and how much tax will be deducted from your salary based on them.Income on which you pay Tax
Besides the salary income you receive, you may be earning an income from several other sources. Your Total Income is the sum total of all heads of income below.Sources of Income
| Income from Salary | Salary, Allowances, Leave encashment basically all the money you receive while rendering your job as a result of your employment agreement |
| Income from House Property | Income from house or building, this may be owned and self-occupied or may be rented |
| Income from Capital Gain | Income from gain or loss when you sell a capital asset |
| Income from Business or Profession | Income/loss that arises as a result of carrying on a business or profession |
| Income from Other Sources |
This is the residual head - includes your income from savings bank accounts,fixed deposits,family pension or gifts received. |
Deductions
Deductions reduce your Gross Income. These are the amounts Income Tax Department allows you to reduce your Income, bringing down your tax liability.
The more you make use of the deductions allowed, the lower your tax shall be. Deductions are allowed under section 80 of the Income Tax Act (Section 80C to 80U).
Make Section 80C your best friend
Section 80C can take off INR 1,50,000 from your Gross Income. Given below are some of the widely-used investment vehicles under this section.
One of the most popular deductions under 80C is deposits to Public Provident Fund or PPF. When you open a PPF account, you need to deposit a minimum of INR 500 and a maximum of INR 1,50,000 in a year. Money deposited in a PPF account compounds, as you deposit more money in the subsequent financial years to claim deductions. PPF is a traditional and safe saving avenue to park your hard earned money. A PPF account can be easily opened with a bank.
b. Tax-saving FD
Fixed deposits assure capital protection as well as a sizable interest income for investors. To get tax benefits under 80C, you need to stay invested for at least 5 years. It is safe, but the Interest Income from it is taxable.
TDS or Tax deducted at source
TDS is Tax Deducted at Source – it means that the tax is deducted by the person making payment. The payer has to deduct an amount of tax based on the rules prescribed by the income tax department. For instance, An employer will estimate the total annual income of an employee and deduct tax on his Income if his Taxable Income exceeds INR 2,50,000. Tax is deducted based on which tax slab you belong to each year. Similarly, if you earn interest from a Fixed Deposit, the bank also deducts TDS. Since the bank does not know your tax slabs, they usually deduct TDS @ 10%, unless you have not mentioned your PAN (in that case a 20% TDS may be deducted).
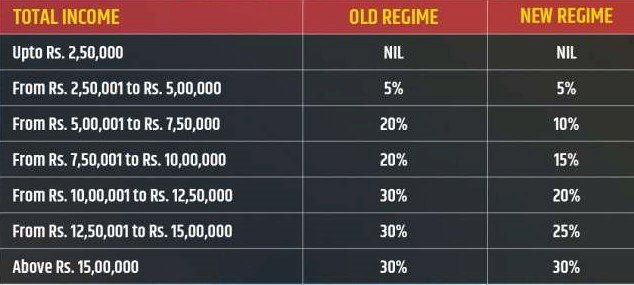
Calculating Tax Payable
On your Taxable Income, tax slabs or rates are applied and final tax payable is calculated. From this tax payable, you can reduce all the TDS that has been already deducted.
Standard Deduction
As per the Budget 2019, salaried employees are entitled to a standard deduction of Rs 50,000 from the gross salary.
What's Your Reaction?